SciFlow project using Parsl to execute Scientific Workflows on HPC resources
19 Jan 2021 - Amanda Wijewickrama and Rajini Wijayawardana, University of Colombo School of Computing, Sri Lanka
The majority of tasks that we, as researchers and analysts, perform, are conveniently expressible as scientific workflows. These workflows provide abstraction, integration and reusability, thereby easing the scientific knowledge discovery process. However, as the complexity of the scientific problem increases, the complexity of the workflow too increases proportionately. To facilitate such interactions, workflows utilize complex connectors.
The SciFlow framework provides a set of compositional channel connectors in a control thread, which can be used to construct a variety of workflow patterns. We separate computational components from coordination components by writing a separate control thread to provide easier workflow modification and computational module reusability to users.
SciFlow is a flexible workflow management system that can be executed on a multitude of High Performance Computing (HPC) resources thanks to the implicit parallelism that Parsl provides.
SciFlow Workflow Connectors
A SciFlow workflow is constructed by stringing together individual Python-Parsl computational units, coordinated by a Golang control thread using ‘connectors’. With SciFlow’s channel connectors, the user is able to connect computational components in a variety of commonly used workflow patterns, as suited to his application.
The diagram below depicts an example scientific workflow, which makes use of three SciFlow connector types.
- Sequence Connector for sequential execution of workflow modules
- Parallel Split Connector to split the coordination thread into concurrent modules
- Exclusive Choice Connector to enforce dynamic decision making.
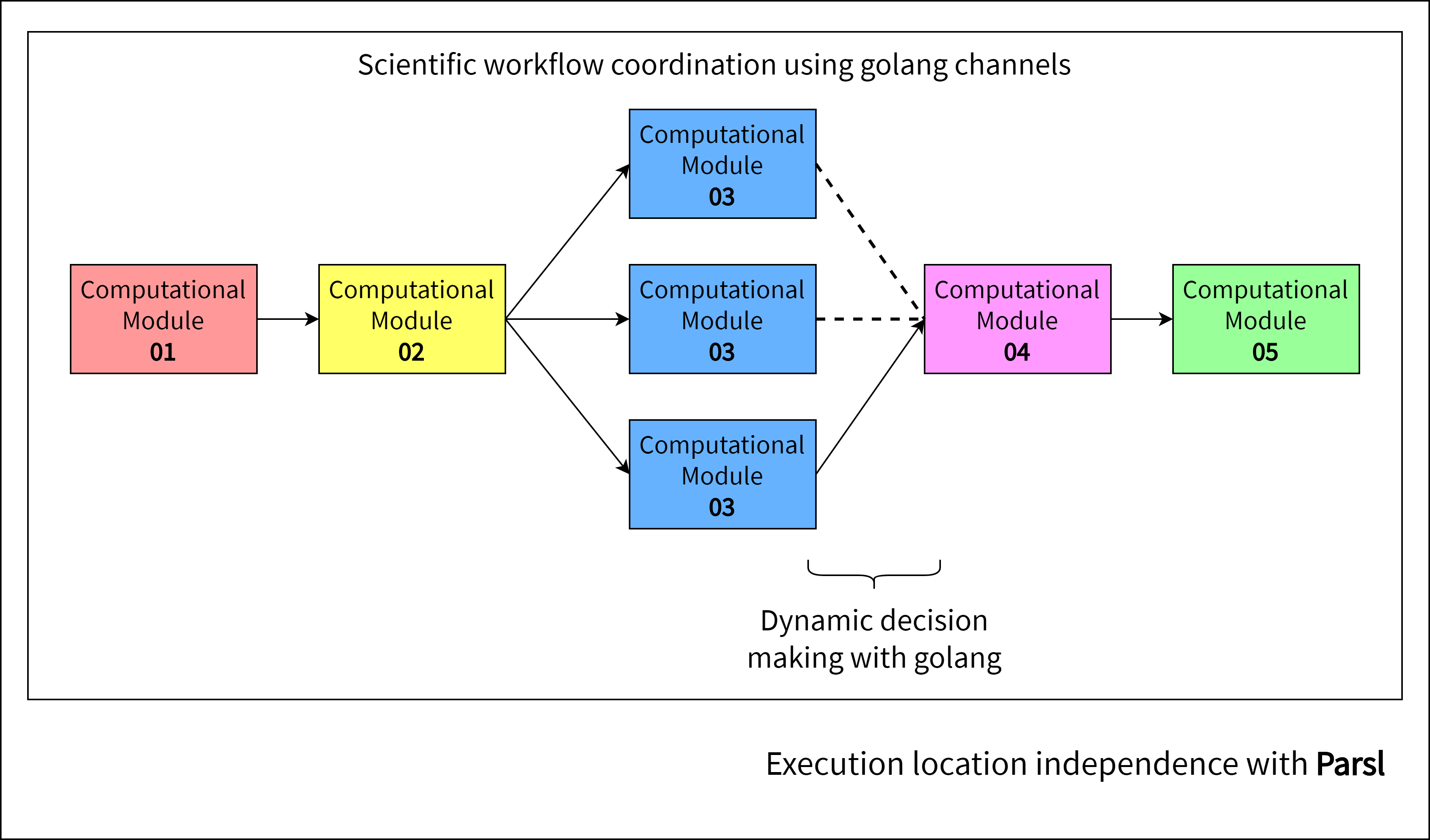
SciFlow focuses on dynamic decision making, where the outcome of an intermediary workflow component would be used to determine the path that the remainder of the workflow would take. This is facilitated by automating the workflow to run a number of times parallely, with different parameters. Connectors can be used to select the best performing parameter set based on some performance matrix, which modifies the workflow path to yield better quality results.
Parsl in SciFlow
The use of Parsl in SciFlow is two fold; to perform data parallelism on individual computational components and to provide execution-location independence for the entire workflow.
Execution location independence
The primary objective of SciFlow is to provide a layer of abstraction to scientific users, so that they could better focus their energies on developing innovative solutions to challenging domain problems, with a lower learning curve for HPC. Through the integration of Parsl to SciFlow, our users are able to harness the full potential of cluster resources for their workflow applications, without the inherent MPI programming burden involved.
With Parsl’s implicit parallelism, we are able to orchestrate the workflow on any HPC resource with minor code changes. During the initial stages of the SciFlow project, we made use of the parallel threads on a local computer, and later moved to a more powerful Beowulf cluster. This goes to show that Parsl’s execution location independence allows its users to start small and scale-out with minimal effort, as the project progresses.
Data parallelism
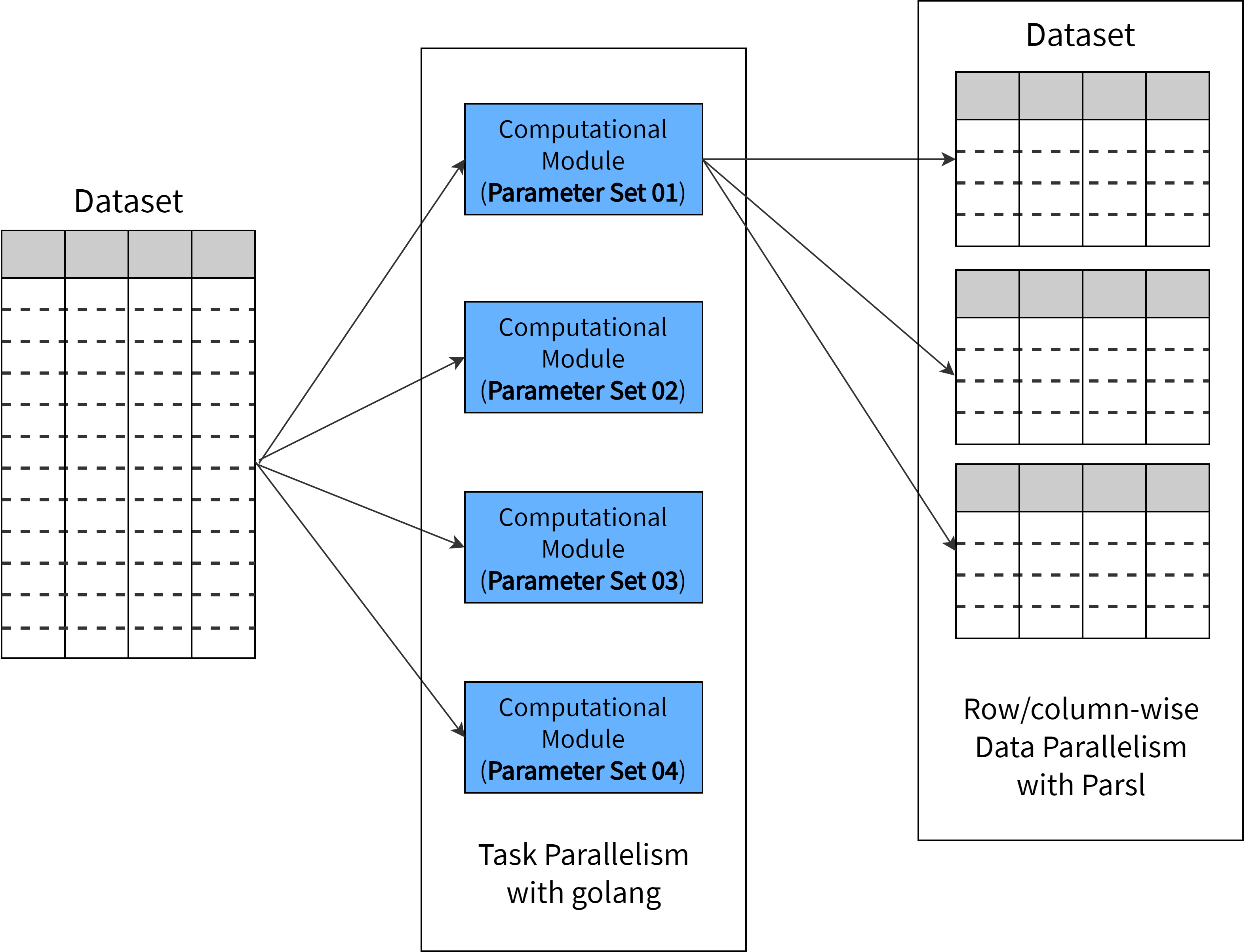
The scientific workflow applications SciFlow caters to make use of large datasets. Therefore, we employ both data and task parallelism to improve computational efficiency. The framework executes computational modules concurrently using the Golang control thread, thereby providing task parallelism. This proves to be extremely helpful in situations similar to hyper parameter optimisation. Using SciFlow and Parsl, the user has the ability to divide the dataset either horizontally or vertically as suited, to achieve data parallelism.
The diagram below depicts this process, where task parallelism is achieved with Golang and data parallelism with Parsl.
Conclusion
SciFlow brings together the concepts of scientific workflow management and implicit parallelism to create an enhanced method for constructing dynamic workflows. This improved performance has been observed through case studies in data analytics and combinatorial optimization. The benefits of parallelism are apparent in such projects owing to the large data volumes and high processing power required.
Parsl allows the SciFlow workflow management framework to scale out easily on a range of HPC resources, while reaping the benefits of data parallelization in computational modules. Parsl’s implicit parallelism makes complex computational resources accessible with minimal effort to domain users, irrespective of their HPC knowledge.
Further details of the SciFlow framework can be found at https://sciflow-fyp.github.io.
Please feel free to reach out to us at sciflowframework@gmail.com.