Parsl and Globus Compute
26 Jun 2024 - Reid Mello (Globus)
Globus Compute provides a unified interface for securely and reliably accessing remote compute resources, from laptops to campus clusters, clouds, and supercomputers. Users expose their resources as function-serving endpoints by installing the Globus Compute endpoint agent, which utilizes Parsl to handle the various execution models of each resource. At a high level, we can conceptualize Globus Compute as an extension of Parsl, transforming a distributed network of Parsl executors into a Function as a Service (FaaS) platform.
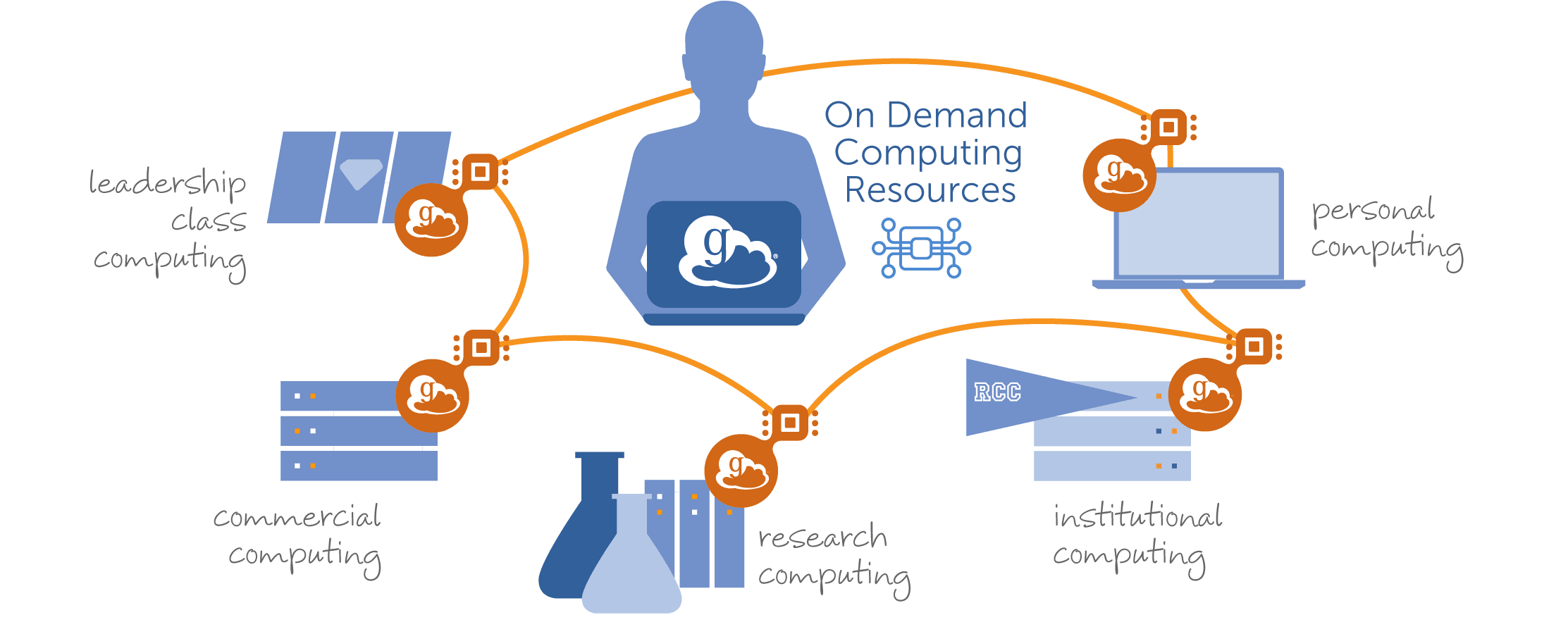
Let’s walk through a simple example to help illustrate how this works. Imagine you are a researcher performing compute-intensive tasks on experiment data. You have secured allocations on Polaris at ALCF and Perlmutter at NERSC, and are looking for a platform to help construct a workflow to simultaneously utilize both systems. You are familiar with Parsl and want to run the workflow from your laptop, so Globus Compute is a natural choice.
First, you will need to pip install globus-compute-endpoint on each allocation. Polaris uses a PBS scheduler, while Perlmutter uses Slurm. The YAML configuration file for your Polaris endpoint might look like the following:
display_name: My Polaris Endpoint
engine:
type: GlobusComputeEngine
max_workers_per_node: 1
address:
type: address_by_interface
ifname: bond0
provider:
type: PBSProProvider
account: example_alcf_account
queue: preemptable
cpus_per_node: 32
select_options: ngpus=4
scheduler_options: "#PBS -l filesystems=home:grand:eagle"
worker_init: "module load Anaconda; source activate compute_venv"
walltime: 01:00:00
nodes_per_block: 1
init_blocks: 0
min_blocks: 0
max_blocks: 2
launcher:
type: MpiExecLauncher
bind_cmd: --cpu-bind
overrides: --depth=64 --ppn 1
When activated, this Globus Compute endpoint will launch a GlobusComputeEngine, which subsequently launches Parsl’s HighThroughputExecutor, PBSProProvider, and MpiExecLauncher. In this example, the only configuration option that the endpoint will not pass through to Parsl is display_name, which specifies the name that is visible in the Globus Compute web interface.
You may also want to share access to your endpoints with specific research colleagues using Globus Auth. You can do this by setting the multi_user configuration option to true, then modifying a few other files. The details on multi-user endpoints are beyond the scope of this blog post, but you can learn more here.
On the client side, Parsl apps and the Globus Compute SDK can work well together. For example, Parsl apps can delegate tasks to Globus Compute endpoints:
import pathlib
import globus_compute_sdk as gc
import parsl
polaris_gce = gc.Executor(endpoint_id=...)
perlmutter_gce = gc.Executor(endpoint_id=...)
def pre_process(data):
...
return data
def analysis(data):
...
return data
@parsl.join_app
def run_pre_process(data):
return perlmutter_gce.submit(pre_process, data)
@parsl.join_app
def run_analysis(data):
return polaris_gce.submit(analysis, data)
@parsl.python_app
def post_process(data):
...
return data
futures = []
dir_path = pathlib.Path("./experiments")
with parsl.load():
for file_path in dir_path.iterdir():
data = file_path.read_text()
futures.append(post_process(analysis(pre_process(data))))
for f in as_completed(futures):
print(f.result())
This workflow delegates pre-processing to your Globus Compute endpoint on Perlmutter at NERSC, analysis to your endpoint on Polaris at ALCF, and post-processing to Parsl workers on your local machine. We utilize Parsl’s @join_app decorator to avoid allocating Parsl workers while waiting for task results from your Globus Compute endpoints.
It is also possible to launch Parsl workflows from within Globus Compute tasks. The recommended setup is to run a Globus Compute endpoint on a login node with default configuration, then submit a task containing the entire Parsl workflow. You can learn more about this methodology here.
The final step is to kick back, grab a drink, and wait for your distributed workflow to return some groundbreaking results. You can rely on Parsl and Globus Compute to handle the rest.
Interoperability between these platforms will continue to expand over the next few years, enabling new and exciting capabilities for researchers. We will do our best to keep this blog up-to-date as we roll out related features and improvements.
👋 Until next time.